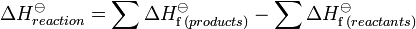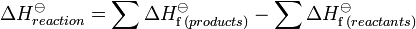Hess' law states that the energy change for any chemical or physical process is independent of the pathway or number of steps required to complete the process provided that the final and initial reaction conditions are the same. In other words, an energy change is path independent, only the initial and final states being of importance. This path independence is true for all state functions.
Hess' law allows the enthalpy change (ΔH) for a reaction to be calculated even when it cannot be measured directly. This is accomplished by performing basic algebraic operations based on the chemical equation of reactions using previously determined values for the enthalpies of formation.
Addition of chemical equations may lead to a net equation. If enthalpy change is known for each equation, the result will be the enthalpy change for the net equation. If the net enthalpy change is negative (ΔHnet < 0), the reaction is exothermic and is more likely to be spontaneous; positive ΔH values correspond to endothermic reactions. Entropy also plays an important role in determining spontaneity, as some reactions with a positive enthalpy change are nevertheless spontaneous.
Hess' Law states that enthalpy changes are additive. Thus the ΔH for a single reaction can be calculated from the difference between the heat of formation of the products and the heat of formation of the reactants: