In Roman mythology, Pluto (Greek: Hades) is the god of the underworld. The planet received this name (after many other suggestions) perhaps because it's so far from the Sun that it is in perpetual darkness and perhaps because "PL" are the initials of Percival Lowell.
Pluto was discovered in 1930 by a fortunate accident. Calculations which later turned out to be in error had predicted a planet beyond Neptune, based on the motions of Uranus and Neptune. Not knowing of the error, Clyde W. Tombaugh at Lowell Observatory in Arizona did a very careful sky survey which turned up Pluto anyway.
After the discovery of Pluto, it was quickly determined that Pluto was too small to account for the discrepancies in the orbits of the other planets. The search for Planet X continued but nothing was found. Nor is it likely that it ever will be: the discrepancies vanish if the mass of Neptune determined from the Voyager 2 encounter with Neptune is used. There is no Planet X. But that doesn't mean there aren't other objects out there, only that there isn't a relatively large and close one like Planet X was assumed to be. In fact, we now know that there are a very large number of small objects in the Kuiper Belt beyond the orbit of Neptune, some roughly the same size as Pluto.
Read more about Pluto l Pluto facts, pictures and information. by nineplanets.org
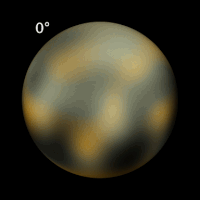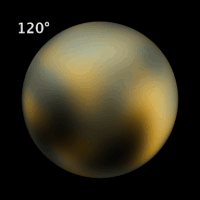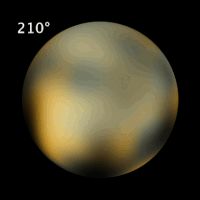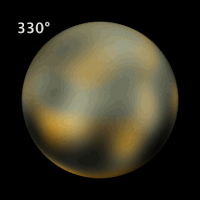
Pluto has not yet been visited by a spacecraft. Even the Hubble Space Telescope can resolve only the largest features on its surface (left and above). A spacecraft called New Horizons was launched in January 2006. If all goes well it should reach Pluto in 2015.
Fortunately, Pluto has a satellite, Charon. By good fortune, Charon was discovered (in 1978) just before its orbital plane moved edge-on toward the inner solar system. It was therefore possible to observe many transits of Pluto over Charon and vice versa. By carefully calculating which portions of which body would be covered at what times, and watching brightness curves, astronomers were able to construct a rough map of light and dark areas on both bodies.
 In late 2005, a team using the Hubble Space Telescope discovered two additional tiny moons orbiting Pluto. Provisionally designated S/2005 P1 and S/2005 P2, they are now known as Nix and Hydra. They are estimated to be between 50 and 60 kilometers in diameter.
In late 2005, a team using the Hubble Space Telescope discovered two additional tiny moons orbiting Pluto. Provisionally designated S/2005 P1 and S/2005 P2, they are now known as Nix and Hydra. They are estimated to be between 50 and 60 kilometers in diameter.
Pluto's radius is not well known. JPL's value of 1137 is given with an error of +/-8, almost one percen
Read more about Pluto l Pluto facts, pictures and information. by nineplanets.org