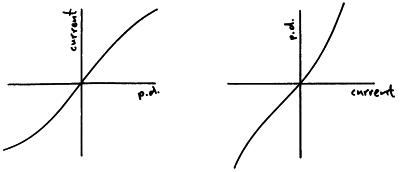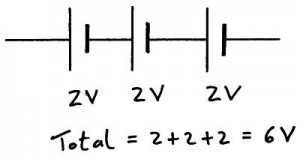Non-ohmic means that current is a more complex function of the applied voltage. LED, LDR
- 1
Non-ohmic Devices
Graphs (potential difference – current characteristics)
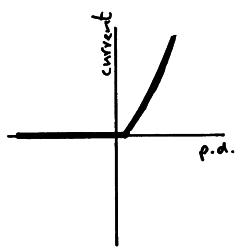
A Filament Lamp
Here the graph curves because as the filament heats it’s resistance goes up.
A diode
A diode only allows current to flow in one direction through it (forward biased), when the current tries to flow the other way (reverse biased) no current is allowed to flow through the diode.
LED – Light Emitting Diode
An Led emits light when a current flows through it.
These are being used more and more for lighting as they require a much smaller current than a filament bulb and that saves energy.
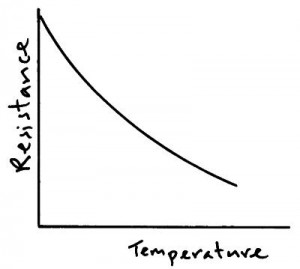
Thermistor
The resistance of a thermistor decreases as it’s temperature increases.
Thermistors can be used as thermostats, the thermistor is used in circuits which monitor and control the temperature of rooms, freezers & fridges etc.
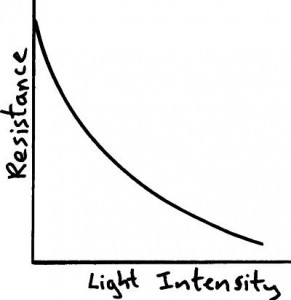
LDR – Light Dependant Resistor
The resistance of an LDR decreases as the light intensity falling on it increases.
LDR’s are used in circuits which automatically switch on lights when it gets dark, for example street lighting.
Cells in Series
When cells are connected in series with each other and they are all connected in the same direction the total potential difference supplied to the circuit is the individual potential differences added together.
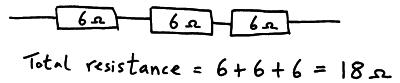
Components in Series
When resistors are in series with each other there total resistance is just there individual resistance added together.
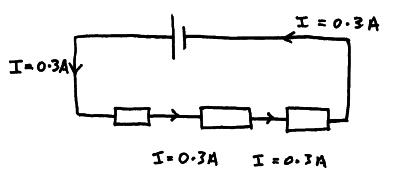
Current in series circuits. When you put an ammeter into a series circuit the current is the same wherever you put the ammeter.
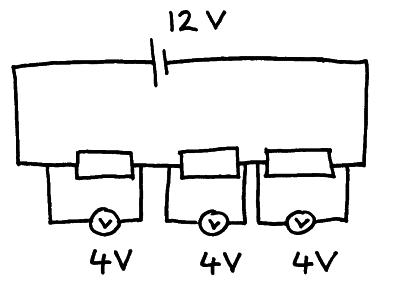
Potential difference in a series circuit. The total potential difference supplied by the cell is divided up between the components. If the components all have the same resistance they will have equal amounts of potential difference across them.
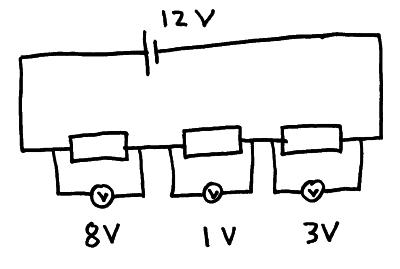
If the resistance are not equal they may have different amounts of potential difference across them but when added up they must always equal the p.d. supplied by the cell.
Components in Parallel
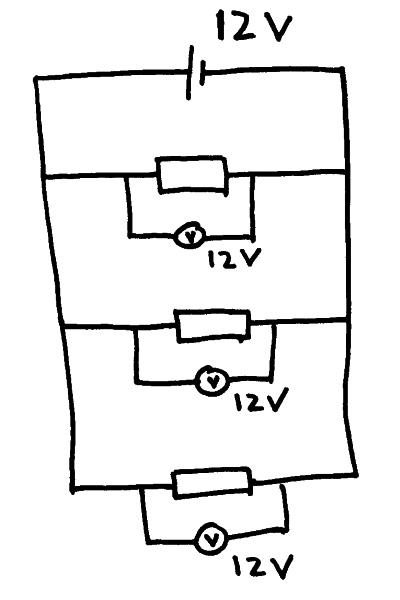
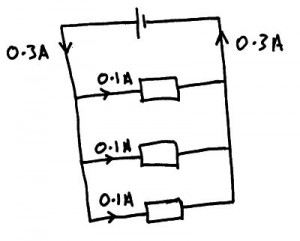
Potential difference in parallel circuits. The potential difference supplied by the cell is the same potential difference as that across each component in the parallel circuit.
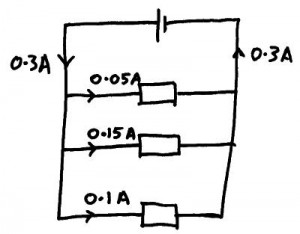
Current in parallel circuits. The total current flowing from the cell must always equal the current flowing through each component when they are added together.
If the components have different resistances then the current through each component may be different but it when you add them together they must add up to the total amount of current leaving the cell.
- 2