a mountain or hill, typically conical, having a crater or vent through which lava, rock fragments, hot vapor, and gas are being or have been erupted from the earth's crust.
- 4
A volcano is an opening, or rupture, in a planet's surface or crust, which allows hot magma, volcanic ash and gases to escape from the magma chamber below the surface.
- 1

A volcano is a landform that results from magma (molten rock within the earth) erupting at the surface. The size and shape of a volcano reflect how often it erupts, the size and type of eruptions, and the composition of the magma it produces.
Magma, lava or tephra?
Molten rock is called magma when it is beneath the earth’s surface. When it is erupted and flows through a volcanic vent it is called lava. And when it is erupted explosively as shattered fragments hurled into the air it is called tephra (which includes volcanic ash, pumice and scoria).
- 1
A volcano is a landform (usually a mountain) where molten rock erupts through the surface of the planet.
In simple terms a volcano is a mountain that opens downward to a pool of molten rock (magma) below the surface of the earth. It is a hole in the Earth from which molten rock and gas erupt.The name "volcano" has its origin from the name of Vulcan, a god of fire in Roman mythology. There are around 1510 'active' volcanoes in the world. We currently know of 80 or more which are under the oceans.
- 1
A volcano is a landform that results from magma (molten rock within the earth) erupting at the surface. The size and shape of a volcano reflect how often it erupts, the size and type of eruptions, and the composition of the magma it produces.
Magma, lava or tephra?
Molten rock is called magma when it is beneath the earth’s surface. When it is erupted and flows through a volcanic vent it is called lava. And when it is erupted explosively as shattered fragments hurled into the air it is called tephra (which includes volcanic ash, pumice and scoria).
- 1
Volcanoes are destructive forces of nature that occur not only on our planet, but also on other planets in our Solar System
Read more: http://www.universetoday.com/38715/volcanoes-for-kids/#ixzz2OWco5i3a
- 1
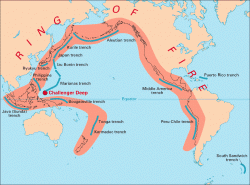
Ring of Fire Volcanoes
Volcanoes are destructive forces of nature that occur not only on our planet, but also on other planets in our Solar System.
Read more: http://www.universetoday.com/38715/volcanoes-for-kids/#ixzz2OWdtGEFv
- 1
Volcanoes
What is a volcano?
A volcano is a mountain that opens downward to a pool of molten rock below the surface of the earth. When pressure builds up, eruptions occur. Gases and rock shoot up through the opening and spill over or fill the air with lava fragments. Eruptions can cause lateral blasts, lava flows, hot ash flows, mudslides, avalanches, falling ash and floods. Volcano eruptions have been known to knock down entire forests. An erupting volcano can trigger tsunamis, flash floods, earthquakes, mudflows and rockfalls.
Click Here to learn more about volcanoes from USGS.
How are volcanoes formed?
Volcanoes are formed when magma from within the Earth's upper mantle works its way to the surface. At the surface, it erupts to form lava flows and ash deposits. Over time as the volcano continues to erupt, it will get bigger and bigger.
What are the different stages of volcanoes?
Scientists have categorized volcanoes into three main categories: active, dormant, and extinct. An active volcano is one which has recently erupted and there is a possibility that it may erupt soon. A dormant volcano is one which has not erupted in a long time but there is a possibility it can erupt in the future. An extinct volcano is one which has erupted thousands of years ago and there’s no possibility of eruption.
Why do volcanoes erupt?
The Earth's crust is made up of huge slabs called plates, which fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. These plates sometimes move. The friction causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions near the edges of the plates. The theory that explains this process is called plate tectonics.
What are plate tectonics?
The theory of plate tectonics is a interesting story of continents drifting from place to place breaking apart, colliding, and grinding against each other. The plate tectonic theory is supported by a wide range of evidence that considers the earth's crust and upper mantle to be composed of several large, thin, relatively rigid plates that move relative to one another. The plates are all moving in different directions and at different speeds. Sometimes the plates crash together, pull apart or sideswipe each other. When this happens, it commonly results in earthquakes.
 |
| Continental Drift: To see this animation again, just refresh this page!This animation shows you what our planet looked like millions of years ago and what it looks like now! (Graphic Credit: Geology Department at University of California, Berkeley) |
Click Here to learn more about plate tectonics and the drifting of our continents.
How many volcanoes are there?
There are more than 1500 active volcanoes on the Earth. We currently know of 80 or more which are under the oceans. Active volcanoes in the U.S. are found mainly in Hawaii, Alaska, California, Oregon and Washington.
What are the different types of volcanoes?
Volcanoes are grouped into four types: cinder cones, composite volcanoes, shield volcanoes and lava volcanoes.
| Cinder Cones | Cinder cones are circular or oval cones made up of small fragments of lava from a single vent that have been blown into the air, cooled and fallen around the vent. |
Composite Volcanoes | Composite volcanoes are steep-sided volcanoes composed of many layers of volcanic rocks, usually made from high-viscosity lava, ash and rock debris. Mt. Rainier and Mount St. Helens are examples of this type of volcano. |
Shield Volcanoes | Shield volcanoes are volcanoes shaped like a bowl or shield in the middle with long gentle slopes made by basaltic lava flows. Basalt lava flows from these volcanoes are called flood basalts. The volcanoes that formed the basalt of the Columbia Plateau were shield volcanoes. |
| Lava Volcanoes | Lava domes are formed when erupting lava is too thick to flow and makes a steep-sided mound as the lava piles up near the volcanic vent. The eruption of Mount St. Helens in 1980 was caused in part by a lava dome shifting to allow explosive gas and steam to escape from inside the mountain. |
What is the difference between lava and magma?
Magma is liquid rock inside a volcano. Lava is liquid rock (magma) that flows out of a volcano. Fresh lava glows red hot to white hot as it flows.
Why does lava take a long time to cool down?
Lava cools slowly because lava is a poor conductor of heat. Lava flows slow down and thicken as they harden.
What is a pyroclastic flow?
A pyroclastic flow is a fluidized mixture of solid to semi-solid fragments and hot, expanding gases that flows down the sides of a volcano. These awesome features are heavier-than-air emulsions that move much like a snow avalanche, except that they are fiercely hot, contain toxic gases, and move at phenomenal, hurricane-force speeds. They are the most deadly of all volcanic phenomena. 
What is lahar?
A lahar is a type of mudflow or debris flow composed of pyroclastic material, rocky debris, and water. The material flows down from a volcano, typically along a river valley. It is very dangerous because it's consistency and the way it acts is very much like cement. It is liquid when it's moving, but when it stops, it solidifies. This can cause just as much devastation as lava itself. 
What is pumice?
Pumice is a light, porous volcanic rock that forms during explosive eruptions. It resembles a sponge because it consists of a network of gas bubbles frozen amidst fragile volcanic glass and minerals. All types of magma (basalt, andesite, dacite, and rhyolite) will form pumice. 
What is the largest active volcano?
The world's largest, active volcano is Mauna Loa in Hawaii, where famous coffee is grown in the rich volcanic soils. Mauna Loa is 13,677 feet above sea level. From its base below sea level to its summit, Mauna Loa is taller than Mount Everest. 
What is the Ring of Fire?
The Pacific Ring of Fire is an area of frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions encircling the basin of the Pacific Ocean. The Ring of Fire has 452 volcanoes and is home to over 50% of the world's active and dormant volcanoes. Ninety percent of the world's earthquakes and 81% of the world's largest earthquakes occur along the Ring of Fire.
When did Mount St. Helens erupt?
On May 18, 1980, Mount St. Helens erupted. It's located in southwestern Washington State in the Cascade Range. The blast was heard as far away as Montana, Idaho, Canada and California. Fifty-seven people died and the eruption caused $1.2 billion in damage.
Click Here to learn more about Mount St. Helens.
Click Here for more info on Mount St. Helens.
What are some other notable volcano eruptions?
Krakatoa was a dormant volcano in Indonesia, which awakened and produced one of the biggest volcanic eruptions in 1883. So massive was the eruption that the sound of it was heard as far away as Australia. It’s widely reported as the loudest sound heard in recorded history. The Krakatoa eruption created a huge amount of ash cloud which covered the Earth and reduced global temperatures for 5 years! A total of 40,000 people died in that explosion and an entire chain of the volcanic island was destroyed. For more info: Click Here!
Mount Pelee was a dormant volcano situated in the Caribbean island of Martinique. In 1902, it erupted in a massive horizontal explosion sending huge clouds of ash released towards the nearby town of Saint-Pierre. The side of the volcano exploded and lava flowed straight into the town, killing 30,000 people in a matter of minutes. It is regarded as one of the biggest and most devastating volcanic eruptions of the 20th century, a benchmark for future eruptions.
Mount Fujiyama, also popularly known as Mount Fuji, is an active volcano which last erupted in 1708. It is incidentally the tallest mountain in Japan. If you are visiting Tokyo, the capital of Japan, look in the west on a clear day and you will be able to see Mount Fuji. It is an iconic volcano. Mount Fuji is 3,776 meters high and it is snow clad throughout the year, with five lakes surrounding it. Currently in a state of dormancy, there has not been any eruption reported for more than 300 years. The last known eruption lasted for about 3 weeks during which it covered the surrounding villages with ash and cinders. Mount Fuji is now a popular tourist location with a large number of climbers actively scaling the mountain top.
What is a tsunami?
A tsunami is a large ocean wave usually caused by an underwater earthquake or a volcanic explosion. Tsunamis are NOT tidal waves. Tidal waves are caused by the forces of the moon, sun, and planets upon the tides, as well as the wind as it moves over the water. With typical waves, water flows in circles, but with a tsunami, water flows straight. This is why tsunamis cause so much damage! 
.![]() Know the Lingo
Know the Lingo ![]()
MAGMA - Magma is the liquid rock inside a volcano.
LAVA - Lava is the liquid rock (magma) that flows out of a volcano. Lava glows red hot to white hot as it flows.
ACTIVE VOLCANO - An active volcano is one that erupts regularly.
DORMANT VOLCANO - A dormant volcano is one that has not erupted for many years, although there is still some activity deep inside.
EXTINCT VOLCANO - An extinct volcano is a volcano that is no longer active.
GEYSERS - Geysers are springs that throw boiling water high in the air. They are caused by volcanic heat warming trapped ground water.
ASH - Ash are very small fragments of lava or rock blasted into the air by volcanic explosions.
PUMICE - It is a light-colored volcanic rock containing lots of bubbles from trapped gases. ![]() Volcano Safety Tips
Volcano Safety Tips ![]()
PLAN FOR A VOLCANO: First of all, have a disaster plan and know whether or not you are at risk for danger. Be prepared for mudslides, flash floods, earthquakes, ash falling, acid rain and tsunamis. Prepare a disaster supplies kit for your home and car. Include a first aid kit, canned food and a can opener, bottled water, battery-operated radio, flashlight, protective clothing, dust mask, goggles and sturdy shoes. Don't forget, know all of your evacuation routes.
DURING A VOLCANO: Follow the evacuation order issued by authorities. Avoid areas downwind and river valleys downstream of the volcano. If your caught indoors, close all windows and doors, put machinery inside a barn, and bring animals inside. If you’re trapped outdoors, seek shelter indoors. If you’re caught in falling rocks, roll into a ball and protect your head. If you’re caught near a stream, be aware of mudflows and move to higher ground. Protect yourself when ash falls by wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants. Use goggles to protect your eyes. Wear a dust mask and keep car engines off.
AFTER A VOLCANO: Cover you mouth and nose. Volcanic ash can irritate your respiratory system. Wear goggles and protect your eyes. Keep your skin covered. Clear roofs of ash, because the ash is very heavy and can cause the building to collapse.
- 1
Volcano
A volcano is an opening, or rupture, in a planet's surface or crust, which allows hot magma, volcanic ash and gases to escape from the magma chamber below the surface.
- 1

A volcano is an opening, in the planet’s surface which allows hot, molten rock, ash and gases to escape from below the surface.
The name, “volcano” originates from the name Vulcan, a god of fire in Roman mythology. Volcanoes are like giant safety valves that release the pressure that builds up inside the Earth. The Hawaii islands were formed by 5 volcanoes.
Classified by the extent of their activity volcanoes are of four types. An ‘active’ volcano is one that erupts regularly. There are about 500 known active volcanoes on Earth, not counting those that lie beneath the sea.
A ‘dormant’ volcano is one that has not erupted for many years, although there is still some activity deep inside it. An ‘extinct’ volcano is one which has ceased to be active.
A volcanic eruption occurs when hot rocks and lava burst from a volcano; and geysers and springs are actually just volcanoes that throw boiling water high in the air. They are caused by volcanic heat warming trapped ground water.
The liquid rocks inside a volcano are called magma and when it flows out it is called as lava. Fresh lava has temperatures from 700 degrees C to 1200′C and glows red-hot to white hot as it flows. The most dangerous volcanic eruption recorded is the eruption of Mount St. Helens in Washington.
The tallest volcano in the world is the Ojos del Salado, a volcano in Chile. The world’s largest volcano is the Muano Loa in Hawaii.
Volcanoes are generally concentrated on the edge of continents, along the island chain, or beneath the sea forming long mountain ranges. A major part of the world’s active volcanoes above sea level encircle the Pacific Ocean forming the “Ring of Fire.”
Volcanoes can have serious affects on the lands and people around them when they erupt. The destruction they leave in their wake accounts for the total annihilation of the surrounding landscape. Around 2, 00,000 people have lost their lives to volcanic eruptions in the past five hundred years.
Buildings are destroyed, people are rendered homeless, people are killed, plant and animal life are both destroyed and the poisonous gases that emanate from the volcanoes can cause death and diseases like pneumonia in the people who survive it.
However not everything associated with the volcanoes is negative. The crust of the earth exists due to
the large volumes of magma that did not erupt but instead cooled below the surface. It results in rich soil which is good for cultivation.
The volcanic ash that blows out of the volcano increases soil fertility by adding nutrients to the soil. Ground water heated by magma can be tapped for geothermal energy. Most of the metallic minerals like copper, gold, silver, lead and zinc are mined from the magmas found deep within the roots of extinct volcanoes.
With the increasing studies done by scientists on volcanoes it is becoming possible to gauge the activity level of a volcano. With this information although it might not be possible to prevent the erupting of a volcano at least the massive destruction of lives can be avoided by getting people evacuated in time.
- 1
Volcanoes are cracks in the Earth's crustout of which magma comes out. This magma comes from the mantle of the Earth and reaches the crust through cracks. Volcanoes are usually found in the form of conical mountains.
A lot of pressure underground pushes up the magma. The magma rushes upwards through a vertical tunnel called a vent and fills the hallow opening called the crater at the top. When the magma reaches the Earth's surface, it is called lava. As lava cools, it solidifies and forms rocks.
- 1
Volcanoes are cracks in the Earth's crustout of which magma comes out. This magma comes from the mantle of the Earth and reaches the crust through cracks. Volcanoes are usually found in the form of conical mountains.
A lot of pressure underground pushes up the magma. The magma rushes upwards through a vertical tunnel called a vent and fills the hallow opening called the crater at the top. When the magma reaches the Earth's surface, it is called lava. As lava cools, it solidifies and forms rocks.
- 1
Volcano, mountain or hill formed by the accumulation of materials erupted through one or more openings (called volcanic vents) in the earth's surface. The term volcano can also refer to the vents themselves. Most volcanoes have steep sides, but some can be gently sloping mountains or even flat tablelands, plateaus, or plains. The volcanoes above sea level are the best known, but the vast majority of the world's volcanoes lie beneath the sea, formed along the global oceanic ridge systems that crisscross the deep ocean floor (see Plate Tectonics). According to the Smithsonian Institution, 1511 above-sea volcanoes have been active during the past 10,000 years, 539 of them erupting one or more times during written history. On average, 50 to 60 above-sea volcanoes worldwide are active in any given year; about half of these are continuations of eruptions from previous years, and the rest are new. Volcanic Eruption The 1983 eruption of Kilauea crater spilled molten, basaltic lava down the flanks of Mauna Loa volcano on Hawaii Island, Hawaii. Hawaiian volcanoes are examples of broad shield volcanoes that form from lava eruptions. Composite volcanoes form when lava eruptions alternate with violent ash eruptions.Soames Summerhays/Photo Researchers, Inc. Expand Volcano © Microsoft Corporation. All Rights Reserved. Expand Volcanic eruptions in populated regions are a significant threat to people, property, and agriculture. The danger is mostly from fast-moving, hot flows of explosively erupted materials, falling ash, and highly destructive lava flows and volcanic debris flows (see Volcano Hazards below). In addition, explosive eruptions, even from volcanoes in unpopulated regions, can eject ash high into the atmosphere, creating drifting volcanic ash clouds that pose a serious hazard to airplanes.
- 1
A volcano is a vent or chimney which transfers molten rock known as magma from depth to the Earth's surface. Magma erupting from a volcano is called lava and is the material which builds up the cone surrounding the vent.
A volcano is active if it is erupting lava, releasing gas or generates seismic activity. A volcano is dormant if it has not erupted for a long time but could erupt again in the future. Once a volcano has been dormant for more than 10 000 years, it is termed extinct.
The explosiveness of a volcanic eruption depends on how easily magma can flow and the amount of gas trapped within the magma. Large amounts of water and carbon dioxide are dissolved in magma causing it to behave in a similar way to gas expanding in fizzy drinks, which forms bubbles and escapes after opening.
As magma rises quickly through the Earth's crust, gas bubbles form and expand up to 1000 times their original size.
Volcanoes can be different in appearance with some featuring perfect cone shapes while others are deep depressions filled with water. The form of a volcano provides a clue to the type and size of its eruption which is controlled by the characteristics and composition of magma. The size, style and frequency of eruptions can differ greatly but all these elements correlated to the shape of a volcano. Three common volcanoes are:
Shield volcanoWhen magma is very hot and runny, gases can escape and eruptions are gentle with considerable amounts of magma reaching the surface to form lava flows. Shield volcanoes have a broad, flattened dome-like shape created by layers of runny lava flowing over its surface and cooling. Because the lava flows easily, it can move down gradual slopes over great distances from the volcanic vents. The lava flows are sufficiently slow for humans to outrun or outwalk them. This type of magma has a temperature between 800°C and 1200°C and is called basaltic magma.
Composite volcano (Strato)Also known as strato-volcanoes, these volcanoes are characterised by an explosive eruption style. When magma is slightly cooler it is thick and sticky, or viscous, which makes it harder for gas bubbles to expand and escape. The resulting pressure causes the magma to foam and explode violently, blasting it into tiny pieces known as volcanic ash. These eruptions create steep sided cones. They can also create lava flows, hot ash clouds called pyroclastic flows and dangerous mudflows called lahars. This type of magma has a temperature between 800°C and 1000°C and is called andesitic magma.
Caldera volcanoThese erupt so explosively that little material builds up near the vent. Eruptions partly or entirely empty the underlying magma chamber which leaves the region around the vent unsupported, causing it to sink or collapse under its own weight. The resulting basin-shaped depression is roughly circular and is usually several kilometres or more in diameter. The lava erupted from caldera volcanoes is very viscous and generally the coolest with temperatures ranging from 650°C to 800°C and is called rhyolitic magma. Although caldera volcanoes are rare, they are the most dangerous. Volcanic hazards from this type of eruption include widespread ash fall, large pyroclastic surges and tsunami from caldera collapse.
Volcanic hazardsVolcanic hazards include explosions, lava flows, bombs or ballistics, ash or tephra, pyroclastic flows, pyroclastic surges, mudflows or lahars, landslides, earthquakes, ground deformation, tsunami, air shocks, lightning, poisonous gas and glacial outburst flooding known as jökulhlaups. Each hazard has a different consequence, although not all occur in all eruptions or in association with all volcanoes.
Volcanic eruptions are measured using a simple descriptive index known as the Volcano Explosivity Index which ranges from zero to eight. The index combines the volume of material ejected with the height of an eruption column and the duration of the eruption.
Interesting fact: Volcanic ash clouds can damage aircraft engines but ash is not visible by radar, the main navigation aid for aircraft. There are nine Volcanic Ash Advisory Centres around the world which use satellites to help track volcanic ash clouds and provide warnings for aircraft.- 1


