Kindly refer to the following link
- 1
water cycle: water is constantly in motion due it evoureporation and condensation.during the day time when it is very hot, water evourporates from rivers,lakes,oceans,etc.and rises as water vappour into the atmoshere .on cooling the water vappour changes back into water droplets and falls on the earth in the form of rain. the entire process of change from one form to another is known as the water cycle.

- -1
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or H2O cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. Water can change states among liquid, vapor, and solid at various places in the water cycle. Although the balance of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time, individual water molecules can come and go, in and out of the atmosphere. The water moves from one reservoir to another, such as from river to ocean, or from the ocean to the atmosphere, by the physical processes of evaporation, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, runoff, and subsurface flow. In so doing, the water goes through different phases: liquid, solid, and gas.
The water cycle involves the exchange of heat energy, which leads to temperature changes. For instance, in the process of evaporation, water takes up energy from the surroundings and cools the environment. Conversely, in the process of condensation, water releases energy to its surroundings, warming the environment. The water cycle figures significantly in the maintenance of life and ecosystems on Earth. Even as water in each reservoir plays an important role, the water cycle brings added significance to the presence of water on our planet. By transferring water from one reservoir to another, the water cycle purifies water, replenishes the land with freshwater, and transports minerals to different parts of the globe. It is also involved in reshaping the geological features of the Earth, through such processes as erosion and sedimentation. In addition, as the water cycle also involves heat exchange, it exerts an influence on climate as well.
- 2
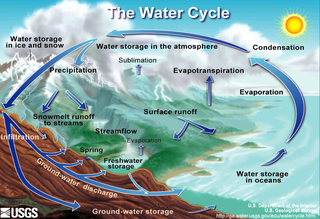 TThe water cycle, also known as thehydrologic cycle or H2O cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. Water can change states among liquid, vapor, and ice at various places in the water cycle. Although the balance of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time, individual water molecules can come and go, in and out of the atmosphere. The water moves from one reservoir to another, such as from river to ocean, or from the ocean to the atmosphere, by the physical processes ofevaporation, condensation, precipitation,infiltration, runoff, and subsurface flow. In so doing, the water goes through different phases: liquid, solid, and gas.
TThe water cycle, also known as thehydrologic cycle or H2O cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. Water can change states among liquid, vapor, and ice at various places in the water cycle. Although the balance of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time, individual water molecules can come and go, in and out of the atmosphere. The water moves from one reservoir to another, such as from river to ocean, or from the ocean to the atmosphere, by the physical processes ofevaporation, condensation, precipitation,infiltration, runoff, and subsurface flow. In so doing, the water goes through different phases: liquid, solid, and gas.
The water cycle involves the exchange of heat energy, which leads to temperature changes. For instance, in the process of evaporation, water takes up energy from the surroundings and cools the environment. Conversely, in the process of condensation, water releases energy to its surroundings, warming the environment. The water cycle figures significantly in the maintenance of life and ecosystems on Earth. Even as water in each reservoir plays an important role, the water cycle brings added significance to the presence of water on our planet. By transferring water from one reservoir to another, the water cycle purifies water, replenishes the land with freshwater, and transports minerals to different parts of the globe. It is also involved in reshaping the geological features of the Earth, through such processes as erosion and sedimentation. In addition, as the water cycle also involves heat exchange, it exerts an influence on climate as well.
- 0
The Water Cycle
Water on Earth is always changing. Its repeating changes make a cycle. As water goes through its cycle, it can be a solid (ice), a liquid (water), or a gas (water vapor). Ice can change to become water or water vapor. Water can change to become ice or water vapor. Water vapor can change to become ice or water.
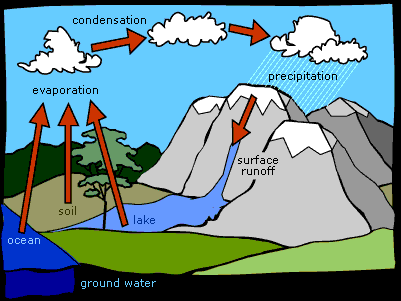
How do these changes happen? Adding or subtracting heat makes the cycle work. If heat is added to ice, it melts. If heat is added to water, it evaporates. Evaporation turns liquid water into a gas called water vapor.
If heat is taken away from water vapor, it condenses. Condensation turns water vapor into a liquid. If heat is taken away from liquid water, it freezes to become ice.
The water cycle is called the hydrologic cycle. In the hydrologic cycle, water from oceans, lakes, swamps, rivers, plants, and even you, can turn into water vapor. Water vapor condenses into millions of tiny droplets that form clouds. Clouds lose their water as rain or snow, which is called precipitation. Precipitation is either absorbed into the ground or runs off into rivers. Water that was absorbed into the ground is taken up by plants. Plants lose water from their surfaces as vapor back into the atmosphere. Water that runs off into rivers flows into ponds, lakes, or oceans where it evaporates back into the atmosphere.
The cycle continues.
- 0
The Water Cycle
Water on Earth is always changing. Its repeating changes make a cycle. As water goes through its cycle, it can be a solid (ice), a liquid (water), or a gas (water vapor). Ice can change to become water or water vapor. Water can change to become ice or water vapor. Water vapor can change to become ice or water.

How do these changes happen? Adding or subtracting heat makes the cycle work. If heat is added to ice, it melts. If heat is added to water, it evaporates. Evaporation turns liquid water into a gas called water vapor.
If heat is taken away from water vapor, it condenses. Condensation turns water vapor into a liquid. If heat is taken away from liquid water, it freezes to become ice.
The water cycle is called the hydrologic cycle. In the hydrologic cycle, water from oceans, lakes, swamps, rivers, plants, and even you, can turn into water vapor. Water vapor condenses into millions of tiny droplets that form clouds. Clouds lose their water as rain or snow, which is called precipitation. Precipitation is either absorbed into the ground or runs off into rivers. Water that was absorbed into the ground is taken up by plants. Plants lose water from their surfaces as vapor back into the atmosphere. Water that runs off into rivers flows into ponds, lakes, or oceans where it evaporates back into the atmosphere.
The cycle continues.
- -1
Water Cycle
water is constantly in motion due it evaporation and condensation.During the day time when it is very hot, water evaporates from rivers,lakes,oceans,etc.and rises as water vapour into the atmoshere .The water vapour forms a thick cloud , when these thick clouds become heavier they cool and the water vapour changes back into water droplets and falls on the earth in the form of rain. the entire process of change from one form to another is known as the water cycle.


- -1
The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle or H2O cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. Although the balance of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time, individual water molecules can come and go, in and out of the atmosphere. The water moves from one reservoir to another, such as from river to ocean, or from the ocean to the atmosphere, by the physical processes of evaporation, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, runoff, and subsurface flow. In so doing, the water goes through different phases: liquid, solid (ice), and gas (vapor).
The water cycle involves the exchange of heat, which leads to temperature changes. For instance, when water evaporates, it takes up energy from its surroundings and cools the environment. When it condenses, it releases energy and warms the environment. These heat exchanges influence climate. By transferring water from one reservoir to another, the water cycle purifies water, replenishes the land with freshwater, and transports minerals to different parts of the globe. It is also involved in reshaping the geological features of the Earth, through such processes as erosion and sedimentation. Finally, the water cycle figures significantly in the maintenance of life and ecosystems on Earth.
- -1
The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle or H2O cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. Although the balance of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time, individual water molecules can come and go, in and out of the atmosphere. The water moves from one reservoir to another, such as from river to ocean, or from the ocean to the atmosphere, by the physical processes of evaporation, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, runoff, and subsurface flow. In so doing, the water goes through different phases: liquid, solid (ice), and gas (vapor).
The water cycle involves the exchange of heat, which leads to temperature changes. For instance, when water evaporates, it takes up energy from its surroundings and cools the environment. When it condenses, it releases energy and warms the environment. These heat exchanges influence climate. By transferring water from one reservoir to another, the water cycle purifies water, replenishes the land with freshwater, and transports minerals to different parts of the globe. It is also involved in reshaping the geological features of the Earth, through such processes as erosion and sedimentation. Finally, the water cycle figures significantly in the maintenance of life and ecosystems on Earth.
- 0


