1 ]An earthquake is a shaking of the ground caused by the sudden breaking and movement of large sections (tectonic plates) of the earth's rocky outermost crust. The edges of the tectonic plates are marked by faults (or fractures). Most earthquakes occur along the fault lines when the plates slide past each other or collide against each other.
The shifting masses send out shock waves that may be powerful enough to
- alter the surface of the Earth, thrusting up cliffs and opening great cracks in the ground and
- cause great damage ... collapse of buildings and other man-made structures, broken power and gas lines (and the consequent fire), landslides, snow avalanches, tsunamis (giant sea waves) and volcanic eruptions.
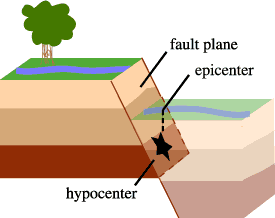 |
Image source: U.S. Geological Survey
Fault or fault plane = the surface where when two blocks of the earth suddenly slip past one another
Hypocenter = the location below the earth’s surface where the earthquake starts
Epicenter = the location on the surface of the earth directly above the hypocenter.
2] A drought is considered a period of abnormally dry weather that causes serious hydrological imbalance in the area.
Historically, droughts affect more people than a heat wave. Not only are there the high temperatures and lack of precipitation, but also the agricultural, economic, and sociopolitical impact on inhabitants within the affected region, as well as those dependent upon goods and services from that area.
Drought areas tend to be warmer than normal for several reasons. One is that the lack of rain-producing clouds allows more sunshine than normal. The other is that the dry ground and parched vegetation result in little evaporation, allowing most of the sun's energy to be used in warming the air. In turn, the increased temperatures result in lower relative humidity, making it less likely to rain.
3] Flooding is when the water level in a creek, river, lake or the sea rises and covers land that is usually dry. Whilst some floods occur without problem, others are devastating, causing large-scale destruction and significant loss of life. Flooding is experienced all over the world and in some countries such as Bangladesh, flooding occurs regularly.
The rise in water level can be due to numerous causes, although the most common in Australia is heavy rainfall. Flooding that is sudden and unexpected is referred to as flash flooding. It is usually caused by slow-moving thunderstorms that deposit an extraordinary amount of water in a relatively short period of time.
Due to its location at the foot of the Illawarra Escarpment, Wollongong is particularly prone to flash flooding. As heavy rainfall occurs along the escarpment, runoff reaches the creeks very quickly, giving local residents little time to prepare.
4] What Are Landslides?![Debris Flow in San Mateo, California [Click on picture for full image]](http://www.ussartf.org/images/debripic.jpg)
Landslides are rock, earth, or debris flows on slopes due to gravity. They can occur on any terrain given the right conditions of soil, moisture, and the angle of slope. Integral to the natural process of the earth's surface geology, landslides serve to redistribute soil and sediments in a process that can be in abrupt collapses or in slow gradual slides. Such is the nature of the earth's surface dynamics. Also known as mud flows, debris flows, earth failures, slope failures, etc., they can be triggered by rains, floods, earthquakes, and other natural causes as well as human-made causes, such as grading, terrain cutting and filling, excessive development, etc. Because the factors affecting landslides can be geophysical or human-made, they can occur in developed areas, undeveloped areas, or any area where the terrain was altered for roads, houses, utilities, buildings, and even for lawns in one's backyard. They occur in all fifty states with varying frequency and more than half the states have rates sufficient to be classified as a significant natural hazard.
 The U.S. Geological Survey, working with other federal agencies, has efforts underway to study, plan, and mitigate landslide risks. So have some communities across the country. Many deal with landslides as part of flood control, erosion control, hillside management, earthquake hazard mitigation, road stabilization, and other programs.
The U.S. Geological Survey, working with other federal agencies, has efforts underway to study, plan, and mitigate landslide risks. So have some communities across the country. Many deal with landslides as part of flood control, erosion control, hillside management, earthquake hazard mitigation, road stabilization, and other programs.
Perhaps the most common reminders of landslide risks are those "Watch For Falling Rocks" highway signs. Although "sliding rocks" is more apt, very few get to see a land slide. Occasionally we see small rocks or debris on the pavement, but a large size slide usually starts with such small incidents. Visually, a landslide resembles a snow avalanche, only with a louder rumbling noise, and is capable of generating enough force and momentum to wipe anything in its path. One such devastating landslide wiped entire towns and villages in Columbia in 1985 when 20,000 died.
![Rockslide on Interstate 70, Colorado [USGS Picture, Click to see larger version]](http://www.ussartf.org/images/RockSlideInterstate70.jpg) The pictures you see on this web site (including the background of this page), are recent examples from around the country. They show what's left after a slide. In some cases, only the rail or pavement is mangled, in others a house or building crushed, but in almost every aftermath, the losses are real, the damages total, and the terrain changes permanent.
The pictures you see on this web site (including the background of this page), are recent examples from around the country. They show what's left after a slide. In some cases, only the rail or pavement is mangled, in others a house or building crushed, but in almost every aftermath, the losses are real, the damages total, and the terrain changes permanent.
Landslides cause one to two billion dollars in damage each year in the US and claim as many as fifty lives. That's more devastating than all the other natural hazards combined. They affect utilities, transportation, and all other forms of infrastructure, whether public or private.
![What are Landslides? by David Miller, USGS [Click to see the document]](http://www.ussartf.org/images/LandslideDiagram.gif) As development pressures around the country increase, so does the likelihood of building in areas susceptible to landslides. Such areas are neither isolated nor far in-between. They span the entire eastern part of US, from New England to the Appalachian region encompassing some of the most scenic areas in the east as well as large urban areas. Landslide risks loom through them all. Pittsburgh and Cincinnati are two examples of urbanized areas with frequent landslides where developments on hills and hillsides are common. In the Great Plains, heavy rains combined with loss of vegetation due to wildfires trigger landslides in clay-rich rocky areas. On the west coast, earthquakes add to the causes of landslides. For example, the 1994 Northridge earthquake triggered many thousand landslides in the Santa Susanna Mountains. In short, no region of the country is safe from landslides, whether caused by geophysical or human-made factors.
As development pressures around the country increase, so does the likelihood of building in areas susceptible to landslides. Such areas are neither isolated nor far in-between. They span the entire eastern part of US, from New England to the Appalachian region encompassing some of the most scenic areas in the east as well as large urban areas. Landslide risks loom through them all. Pittsburgh and Cincinnati are two examples of urbanized areas with frequent landslides where developments on hills and hillsides are common. In the Great Plains, heavy rains combined with loss of vegetation due to wildfires trigger landslides in clay-rich rocky areas. On the west coast, earthquakes add to the causes of landslides. For example, the 1994 Northridge earthquake triggered many thousand landslides in the Santa Susanna Mountains. In short, no region of the country is safe from landslides, whether caused by geophysical or human-made factors.
Although the term landslide is often used somewhat loosely to mean any fairly rapid movement of rocks and sediment downslope, it is actually more accurate to use the term mass wasting to refer to the wide variety of mass movement processes that wear away at the Earth's surface.
5] A volcano can be simply defined as a rupture or an opening on the crust of a planet like earth. This opening allows hot ash, molten rock and gases to blow off from the underground spaces. Volcanoes generally acquire shape of a mountain. Volcanoes are usually found at places where tectonic plates get converged or diverged. But there existence at a particular place depends upon many environmental and geological factors. Volcanoes can also occur at a place because of hot spots or mantle plumes. Even hotspot volcanoes are very common at other planets of solar system especially on moons and rock based planets.
Features of volcanoes
Common features of volcanoes are lava, conical shaped mountain and release of poisonous gases from the carter situated at the summit of the volcanoes. These are most common features attained by almost all of the active volcanoes. But describing complete features of all the volcanoes is a very tedious thing, because shape, attributes and behavior of different volcanoes depends upon different factors. For example some volcanoes have a Steve peak formed as the lava dome on the other hand other possesses a crater at the summit. More exciting types of volcanoes are ice volcanoes (cryovolcanoes) and mud volcanoes, these volcanoes exist on moons of Saturn, Neptune and Jupiter.
6] A tsunami (pronounced tsoo-NAH-mee) is a series of waves, made in an ocean or other body of water by an earthquake, landslide, volcanic eruption, or meteorite impact. Tsunamis can cause huge destruction when they hit coastlines. Some people call tsunamis “tidal waves”, but these large waves really have little to do with tides, so the term “tidal wave” does not really suit them.
Tsunami waves are different from the waves you can usually find rolling into the coast of a lake or ocean. Those waves are made by wind offshore and are quite small compared with tsunami waves. A tsunami wave in the open ocean can be more than 100 km across. That’s roughly the length of 1000 American football fields! Tsunami waves are huge and can travel very quickly, at about 700 km/hr, but they are only about one meter high in the open ocean.
7] Global warming is a topic that is never free from debate, whether you have heard about it by this main buzz word or in relation to others such as 'the greenhouse effect' or even 'climate change' as it is more commonly referred to these days, it is something that never fails to spark controversy when spoken about.
But what is global warming and is global warming real? This site provides a comprehensive guide to the subject of global warming and covers all areas including global warming causes and effects, a wealth of global warming information, as well as a global warming definition and details of the greenhouse gases that are responsible for the change in the earth's climate.
8] Twenty-five years have passed since that night of terror and death in Bhopal, which saw a cloud of deadly gases explode out of a faulty tank in a pesticide factory and silently spread into the homes of sleeping people. Although no official count of casualties has ever been done, estimates based on hospital and rehabilitation records show that about 20,000 people died and about 5.7 lakh suffered bodily damage, making it by far the world's worst industrial disaster ever.



![Debris Flow in San Mateo, California [Click on picture for full image]](http://www.ussartf.org/images/debripic.jpg)

![Rockslide on Interstate 70, Colorado [USGS Picture, Click to see larger version]](http://www.ussartf.org/images/RockSlideInterstate70.jpg)
![What are Landslides? by David Miller, USGS [Click to see the document]](http://www.ussartf.org/images/LandslideDiagram.gif)