explain Thomson's model of an atom...
Thomson atomic model was proposed by William Thomson in the year 1900. This model explained the description of an inner structure of the atom theoretically. It was strongly supported by Sir Joseph Thomson, who had discovered the electron earlier.
During cathode ray tube experiment, a negatively charged particle was discovered by J.J. Thomson. This experiment took place in the year 1897. Cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube. The negative particle was called an electron.
Thomson assumed that an electron is two thousand times lighter than a proton and believed that an atom is made up of thousands of electrons. In this atomic structure model, he considered atoms surrounded by a cloud having positive as well as negative charges. The demonstration of the ionization of air by X-ray was also done by him together with Rutherford. They were the first to demonstrate it. Thomson’s model of an atom is similar to a plum pudding.
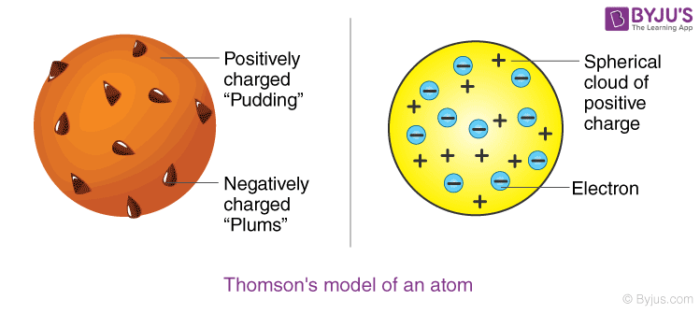


.png)
.png)