how do parkyotic and eukaryotic resemble
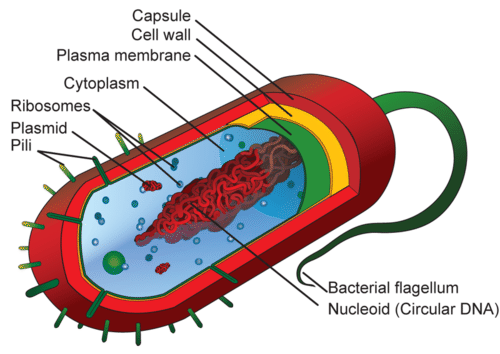
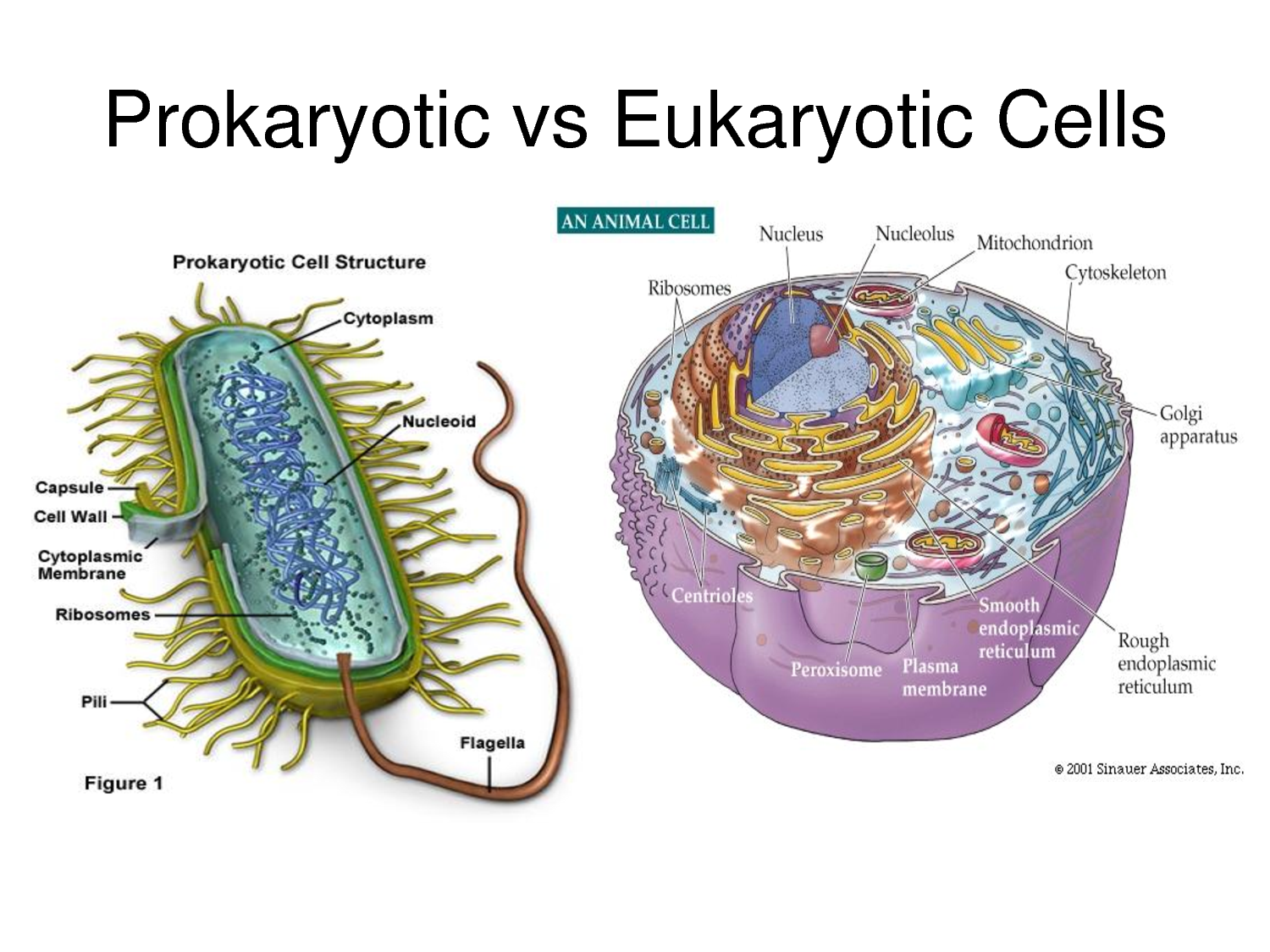
Prokaryotic cells are cells without a nucleus. The DNA in prokaryotic cells is in the cytoplasm rather than enclosed within a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms, such as bacteria, like the one shown in Figure below. Organisms with prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes. They were the first type of organisms to evolve and are still the most common organisms today.
Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a nucleus. A typical eukaryotic cell is shown in Figure below. Eukaryotic cells are usually larger than prokaryotic cells, and they are found mainly in multicellular organisms. Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes, and they range from fungi to people.
Eukaryotic cells also contain other organelles besides the nucleus. An organelle is a structure within the cytoplasm that performs a specific job in the cell. Organelles called mitochondria, for example, provide energy to the cell, and organelles called vacuoles store
substances in the cell. Organelles allow eukaryotic cells to carry out more functions than prokaryotic cells can. This allows eukaryotic cells to have greater cell specificity than prokaryotic cells. Ribosomes, the organelle where proteins are made, are the only organelles in prokaryotic cells.