Please Explain Life Cycle of Plasmodium(Including Exo Erythrocytic, Erythrocytic and sporogonic Cycle) In Complete Detail.
Plasmodium is a pathogenic parasitic protozoan belonging to the genus Plasmodium and containing over 200 species. The most common species being the malarial pathogen. It causes malaria in humans.
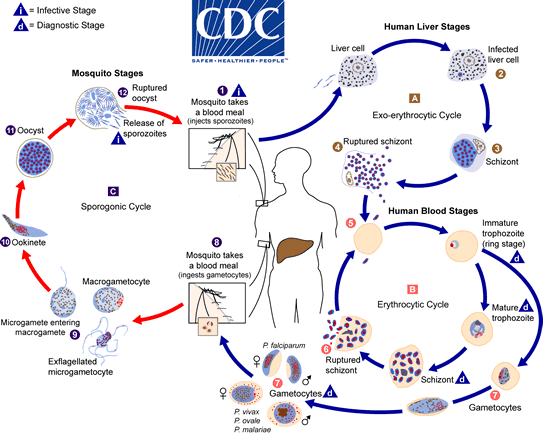
Life cycle of Plasmodium-
Plasmodium requires two hosts to complete its life cycle. * When female Anopheles mosquito bites a healthy human being, it releases Plasmodium, which lives in its body as sporozoite (infectious form). * The parasites multiply (asexual reproduction) in the liver cells and finally burst the liver cells. Sporozoites are released in blood. * Parasites enter RBCs and further multiply (asexual reproduction) here and finally burst RBCs also. * Bursting of RBCs is accompanied by release of a toxic substance called haemozoin (associated with fever and chills). * In the RBCs, only sporozoites change into gametocytes (sexual stage). Gametocytes multiply. * When the diseased person is bitten by a female Anopheles mosquito, gametocytes are introduced into the mosquito. * Gametocytes fertilise and develop inside the intestine of mosquito to form sporozoites. * Sporozoites are stored in the salivary glands of mosquito and are released into the healthy person who is bitten by this mosquito.

The post erythrocytic cycle of Plasmodium is also called as sporogenic cycle.
Regards.