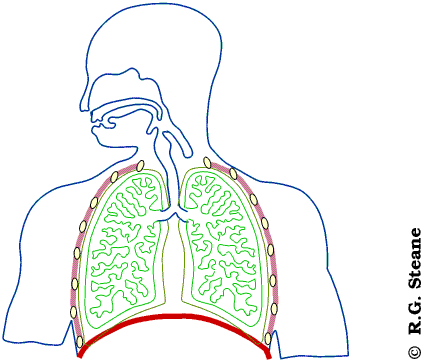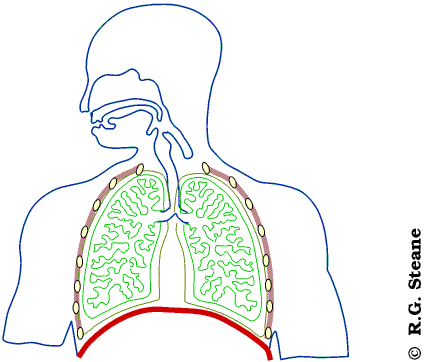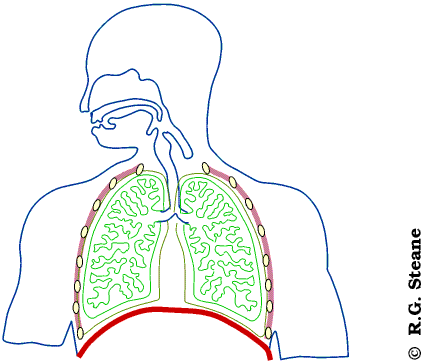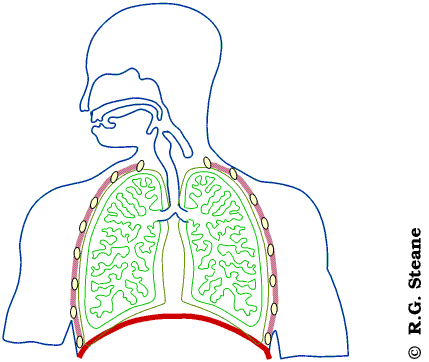
what are the structures used in inhalation and exhalation?
The question that you have asked can be easily answered by going through our study material at the following link and if you face any problems in understanding or answering that question please get back to us.