Saponification is the reaction of higher fatty acids in the presence of alkali (or base) to form soap and glycerol.
The soap thus formed is precipitated with the addition of NaCl.
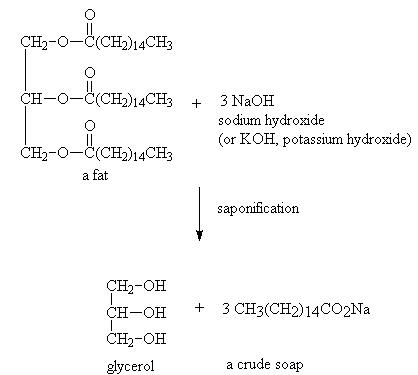
The complete saponification reaction is represented as:
- 0
Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester under basic conditions to form an alcohol and the salt of a carboxylic acid (carboxylates). Saponification is commonly used to refer to the reaction of a metallic alkali (base) with a fat or oil to form soap. Saponifiable substances are those that can be converted into soap.
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a caustic base. If NaOH is used a hard soap is formed, whereas when potassium hydroxide (KOH) is used, a soft soap is formed. Vegetable oils and animal fats are fatty esters in the form of triglycerides. The alkali breaks the ester bond and releases the fatty acid salt and glycerol. If necessary, soaps may be precipitated by salting it out with saturated sodium chloride. The saponification value is the amount of base required to saponify a fat sample.
In a classic laboratory procedure the triglyceride trimyristin is obtained by extracting nutmeg with diethyl ether.Saponification to the sodium salt of myristic acid takes place with NaOH in water. The acid itself can be obtained by adding dilute hydrochloric acid.
ANOTHER DEFINITION FOR SAPONIFICATION
Saponification value (or "saponification number", also referred to as "sap" in short) represents the number of milligrams of potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide required to saponify 1g of fat under the conditions specified. It is a measure of the average molecular weight (or chain length) of all the fatty acids present. As most of the mass of a fat/triester is in the 3 fatty acids, it allows for comparison of the average fatty acid chain length. The long chain fatty acids found in fats have low saponification value because they have a relatively fewer number of carboxylic functional groups per unit mass of the fat as compared to short chain fatty acids. If more moles of base are required to saponify N grams of fat then there are more moles of the fat the chain lengths are relatively small,
- -1
Saponification reaction:
Alcohol and carboxylic acid can be reclaimed from an ester by making it react with an acid or a base. This reaction is used in the preparation of soaps, and is known as saponification reaction.
For example, ethyl acetate (ester) reacts with sodium hydroxide (base) to form ethanol (alcohol) and ethanoic acid (carboxylic acid).

- 1

