With the help of an algebric equation how did hardy weinberg explained that in a guven population the frequency of occurence of alleles of a gene is suppose to remain the same through generations. Although a prokaryotic cell has no defined nucleus yet DNA is not scattered throughout the cell. Explain.
The Hardy Weinberg principle(also known as the Hardy Weinberg equilibrium, model, theorem, or law) states that allele and genotype frequencies in a population will remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of other evolutionary influences. These influences include non-random mating,mutation,selection,genetic drift,gene flow and meiotic drive. Because one or more of these influences are typically present in real populations, the Hardy Weinberg principle describes an ideal condition against which the effects of these influences can be analysed.
In the simplest case of a single locus with two alleles denoted A and a with frequencies f(A) =p and f(a) =q, respectively, the expected genotype frequencies are f(AA) =p2for the AA homo zygotes,f(aa) =q2for the aa homozygotes, and f(Aa) = 2pq for the heterozygotes. The genotype proportions p2, 2pq, and q2are called the Hardy-Weinberg proportions. [Note that the sum of all genotype frequencies of this case is the binomial expansion of the square of the sum of p and q, and such a sum, as it represents the total of all possibilities, must be equal to 1. Therefore(p+q)2=p2+ 2pq+q2= 1. The solution of this equation isq= 1 -p.]
If union of gametes to produce the next generation is random,it can be shown that the new frequency f′satisfies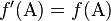 and
and . That is, allele frequencies are constant between generations.
. That is, allele frequencies are constant between generations.
This principle was named after G. H. Hardy and Wilhelm Weinberg, who first demonstrated it mathematically
Regards

