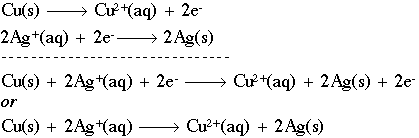Redox ReactionsRedox reactions, oroxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid-base reactions. Fundamentally, redox reactions are a family of reactions that are concerned with the transfer of electrons between species. Like acid-base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set -- you don't have an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening at the same time. Oxidation refers to the loss ofelectrons, while reduction refers to the gain of electrons. Each reaction by itself is called a "half-reaction", simply because we need two (2) half-reactions to form a whole reaction. In notating redox reactions, chemists typically write out the electrons explicitly:
Cu (s) ---- Cu
2++ 2 e
-This half-reaction says that we have solid copper (with no charge) being oxidized (losing electrons) to form a copper ion with a plus 2 charge. Notice that, like thestoichiometrynotation, we have a "balance" between both sides of the reaction. We have one (1) copper atom on both sides, and the charges balance as well. The symbol "e-" represents afree electronwith a negative charge that can now go out and reduce some other species, such as in the half-reaction:
2 Ag
+(aq) + 2 e
------- 2 Ag (s)
Here, two silver ions (silver with a positive charge) are being reduced through the addition of two (2) electrons to form solid silver. The abbreviations "aq" and "s" mean aqueous and solid, respectively. We can now combine the two (2) half-reactions to form a redox equation:
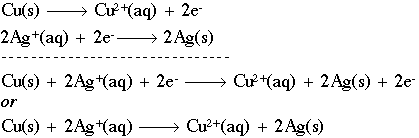
We can also discuss the individual components of these reactions as follows. If a chemical causes another substance to be oxidized, we call it the oxidizing agent. In the equation above, Ag+is the oxidizing agent, because it causes Cu(s) to lose electrons. Oxidants get reduced in the process by a reducing agent. Cu(s) is, naturally, the reducing agent in this case, as it causes Ag+to gain electrons.
.png)