How is cellular respiration related to exchange of respiratory gases?
- 3
The process of releasing energy from food is called respiration.
The process of respiration involves taking in oxygen (of air) into the cells, using it for releasing energy by burning food, and then eliminating the waste products (carbon dioxide and water) from the body.
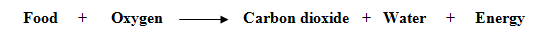
- The process of respiration which releases energy takes place inside the cells of the body. So, it is also known as cellular respiration.
- Respiration is essential for life because it provide energy for carrying out all the life processes which are necessary to keep the organism alive.
Breathing
Respiration
The mechanism by which organisms obtain oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide is called breathing.
Respiration includes breathing as well as the oxidation of food in the cells of the organism to release energy.
Breathing is a physical process.
Respiration includes physical as well as biochemical process of oxidation of food.
The process of breathing involves the lungs of the organism.
The process of respiration involves the lungs and mitochondria of the cells.
How Energy Released during Respiration is Stored:- The energy produced during respiration is stored in the form of ATP molecules in the cells of the body and used by the organism as when required.
- ADP (Adenosine Di-Phosphate, low energy content), Inorganic Phosphate (Pi) and ATP (Adenosine Tri-Phosphate, high energy content) are the substances present inside a cell.
- The energy released during respiration is used to make ATP molecules form ADP and inorganic phosphate.
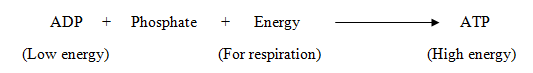
- Thus, energy is stored in the form of ATP.
- When the cell needs energy, then ATP can be broken down using water to release energy. Thus:
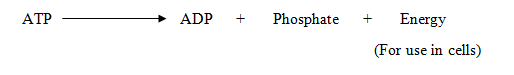
- The energy equivalent to 30.5KJ/mole is released in this process.
- ATP is known as energy currency of cells.
In most of the cases, the organisms carry out respiration by using oxygen. There are, however some organisms which carry out respiration without using oxygen. Based on this, we have two types respiration:
- Aerobic respiration
- Anaerobic respiration
- The respiration which uses oxygen is called aerobic respiration.
- In aerobic respiration, the glucose food is completely broken down into carbon dioxide and water by oxidation.
- Aerobic respiration produces a considerable amount of energy for use by the organism which gets stored in the ATP molecules.
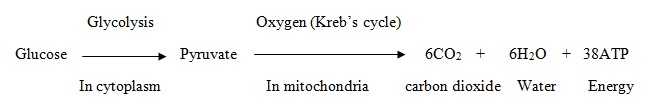
- Mitochondria are the sites of aerobic respiration in the cells. Thus, the breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in mitochondria.
- The respiration which takes place without oxygen is called anaerobic respiration.
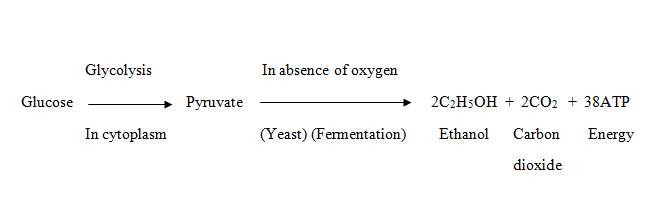
- The microscopic organisms like yeast and some bacteria obtain energy by anaerobic respiration (which is called fermentation).
- In anaerobic respiration, the microorganisms like yeast break down glucose (food) into ethanol and carbon dioxide, and release energy.
- Anaerobic respiration produces much less energy which gets stored in the ATP molecules.
- Sometimes, when there is lack of oxygen in our muscle cells, another pathway for the breakdown of pyruvate is taken. Here the pyruvate is converted into lactic acid (which is also a three-carbon molecule) with the release of small amount of energy.
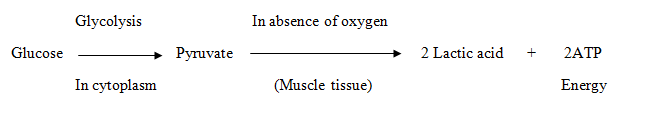 Respiration In Plants
Respiration In Plants
- Like animals, plants also need energy. The plants get this energy by the process of respiration. Plants also use oxygen of air for respiration and release carbon dioxide.
- The respiration in plants differs from the animals in three respects:
Respiration in plants
Respiration in animals
All the parts of a plant (like root, stem and leaves) perform respiration individually.
An animal performs respiration as a single unit.
During respiration in plants, there is a little transport of respiratory gases from one part of the plant to the other.
Respiratory gases are usually transported over long distance inside an animal during respiration.
The respiration in plants occurs at a slow rate.
The respiration in animals occurs at a much faster rate.
Plants get Oxygen by Diffusion:- Plants have a branching shape, so they have quite a large surface area in comparison to their volume. Therefore, diffusion alone can supply all the cells of the plants with as much oxygen as they need for respiration.
- Diffusion occurs in the rots, stems and leaves of plants.
- Air occurs in soil interspaces. Root hairs of the roots are in direct contact with them.
- Oxygen of the soil air diffuses through root hair and reaches all internal cells of the root for respiration.
- Carbon dioxide produced by root cells diffuses in the opposite direction.
- In water-logged conditions, soil air becomes deficient. In the absence of oxygen, metabolic activity of the root declines and the plant may wither.
- The stems of herbaceous plants have stomata. The oxygen from air diffuses into the stem of a herbaceous plant through stomata and reaches all the cells for respiration.
- The carbon dioxide gas produced during respiration diffuses out into the air through the same stomata.
- In woody stems, the bark has lenticels for gaseous exchange.
- The leaves of a plant have tiny pores called stomata. The exchange of respiratory gases in the leaves takes place by the process of diffusion through stomata.
- During day time, when photosynthesis occurs, oxygen is produced. The leaves use some of this oxygen for respiration and rest of the oxygen diffuses out into air.
- Again, during the day time, carbon dioxide produced by respiration is all used up in photosynthesis by leaves. Even more carbon dioxide is taken in from air.
- Thus, net gas exchange in leaves during day time is: O2 diffuses out ; CO2 diffuses in.
- At night time, when no photosynthesis occurs and hence no oxygen is produced, oxygen from air diffuses into leaves to carry out respiration. And carbon dioxide produced by respiration diffuses out into air.
- Thus, net gas exchange in leaves at night is: O2 diffuses in; CO2 diffuses out.
- 2

