An isothermal process is a change of a system, in which the temperature remains constant: ΔT = 0. This typically occurs when a system is in contact with an outside thermal reservoir (heat bath), and the change occurs slowly enough to allow the system to continually adjust to the temperature of the reservoir through heat exchange. In contrast, an adiabatic process is where a system exchanges no heat with its surroundings (Q = 0). In other words, in an isothermal process, the value ΔT = 0 but Q ≠ 0, while in an adiabatic process, ΔT ≠ 0 but Q = 0.
An isobaric process is a thermodynamic process in which the pressure stays constant. The term derives from the Greek isos, (equal), and barus, (heavy). The heat transferred to the system does work but also changes the internal energy of the system:
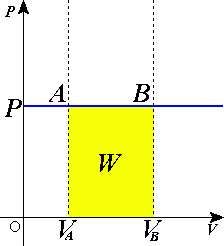
The yellow area represents the work done
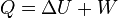
According to the first law of thermodynamics, where W is work done by the system, U is internal energy, and Q is heat. Pressure-volume work by the closed system is defined as:

where Δ means change over the whole process, whereas d denotes a differential. Since pressure is constant, this means that
 .
.
Applying the ideal gas law, this becomes
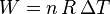
assuming that the quantity of gas stays constant, e.g., there is no phase transition during a chemical reaction. According to the equipartition theorem, the change in internal energy is related to the temperature of the system by
 ,
,
where  is specific heat at a constant volume.
is specific heat at a constant volume.
Substituting the last two equations into the first equation produces:


 ,
,
where  is specific heat at a constant pressure.
is specific heat at a constant pressure.



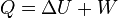

 .
.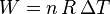
 ,
, is specific heat at a constant volume.
is specific heat at a constant volume.

 ,
, is specific heat at a constant pressure.
is specific heat at a constant pressure.