what is z scheme
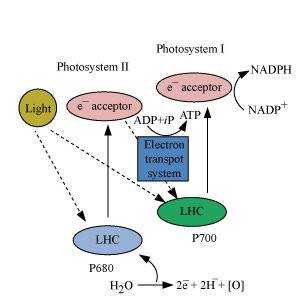
The Z-scheme describes the oxidation/reduction changes during the light reactions of photosynthesis.
PSII absorbs 680 nm wavelength of red light, causing electrons to become excited and jump into an orbit farther from the nucleus.
These electrons are then accepted by an electron acceptor, which sends them to an electron transport system.
Electron transport system transfers the electrons to PSI.
Electrons in PSI are simultaneously excited on receiving a wavelength of 700 nm. These electrons are again transferred to another electron acceptor having a greater redox potential.
From the electron acceptor, electrons are transferred to the molecule of NADP+.
Addition of these electrons reduces the NADP+ to NADPH+ H+.
During this process, electrons move downhill, i.e., towards the systems at greater redox potential.
The flow of electrons assumes the shape of the letter ‘Z’ when all carriers are placed according to their redox potential. Hence, the process is called Z scheme.
.